Dart: Constructor | Default Constructor | Parameterized Constructor | Named Constructor
What is Constructor in Dart?
We can use constructor while creating object.
As we know there are many element is class, and out of all the element the Constructor will run the first among the all element.
What is Default Constructor?
If you don't define any constructor in class, Dart provides a default constructor.
This constructor initializes the object but does not perform any additional tasks.
Example:
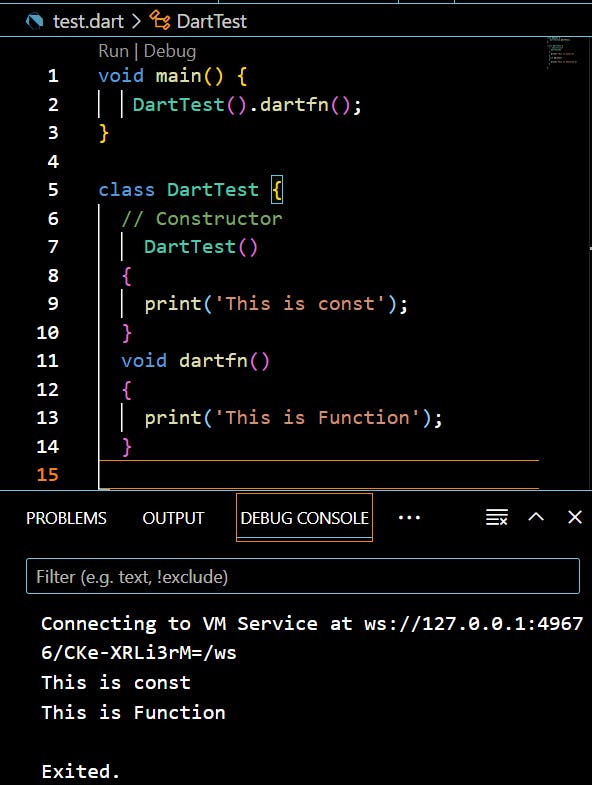
Inside
main(), an object of theDartTestclass is created using the default constructorDartTest().When an object of a class is created in Dart, its constructor is automatically called. In this case, the constructor
DartTest()prints the message'This is const'.After the object is created, the
dartfn()method of theDartTestclass is invoked on that object. This method prints the message'This is Function'.In summary, when the program is executed, it first prints
'This is const'because the constructorDartTest()is called when the object is created. Then, it prints'This is Function'when thedartfn()method is invoked.
What is Parameterized Constructor?
In Dart, you can also create a constructor having some parameters.
These parameters will decide which constructor will be called and which will be not.
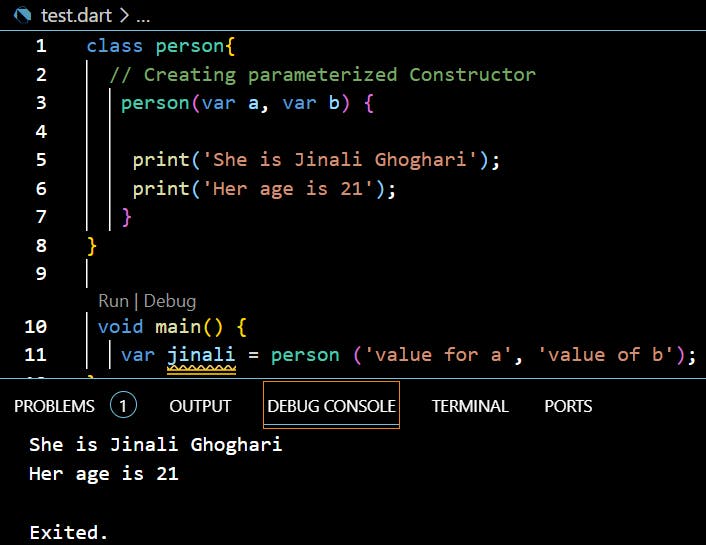
What is Named Constructor?
As you can’t define multiple constructors with the same name, this type of constructor is the solution to the problem.
They allow the user to make multiple constructors with a different name.
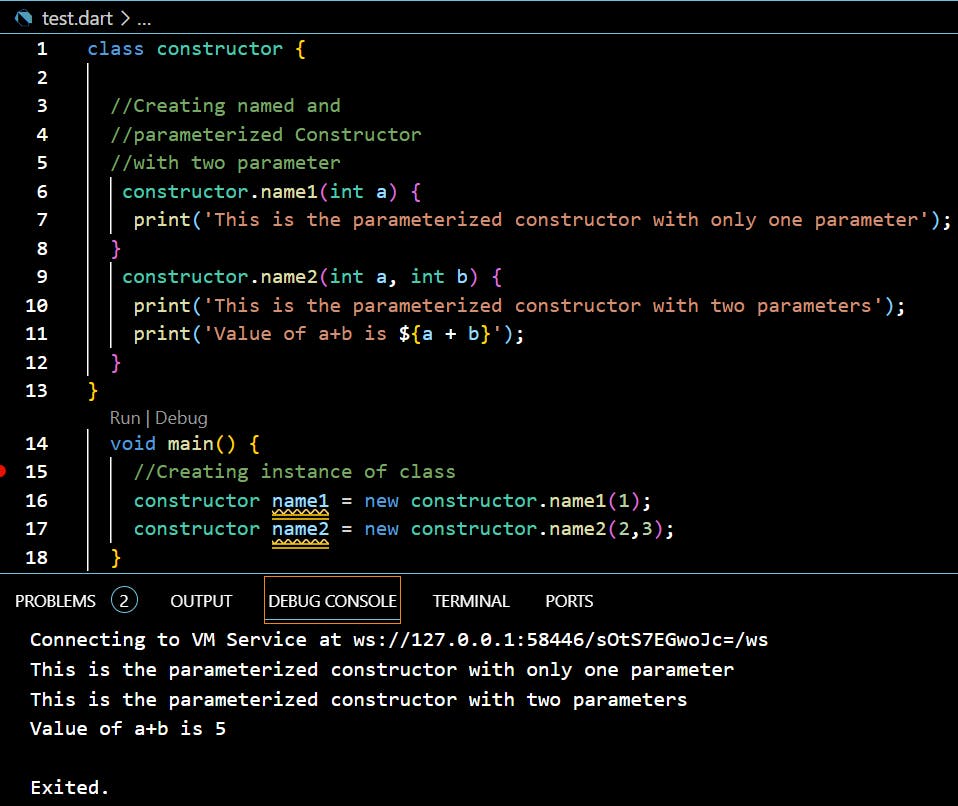
In conclusion, the provided Dart code defines a class
constructorwith two constructorsname1andname2. These constructors demonstrate the concept of named and parameterized constructors in Dart.
